Daily Insights Hub
Your go-to source for the latest news and information.
Nuke Secrets You Didn't Know Existed
Uncover shocking nuclear secrets and hidden truths that will change the way you think about atomic power! Discover the unknown now!
The Hidden History of Nuclear Weapons: Secrets Unveiled
The history of nuclear weapons is rife with secrets that have shaped international relations and global security. From the clandestine operations that led to the Manhattan Project during World War II to the Cold War arms race between superpowers, the narrative is layered with intrigue and complexity. Key figures like J. Robert Oppenheimer and Leo Szilard played pivotal roles, but many contributions remain obscured by time. A deeper exploration reveals the ethical dilemmas and political maneuverings that accompanied the development of these formidable weapons, raising crucial questions about the balance of power and human morality.
Moreover, the hidden history extends beyond mere development; it encompasses the extensive nuclear testing programs conducted in remote locations such as the South Pacific and Nevada. These tests were often shrouded in secrecy, with dire consequences for local populations and the environment. As declassified documents have emerged in recent years, they unveil not only the technical goals of these tests but also the extensive cover-ups and the long-term effects on human health and ecology. Understanding this hidden history is essential for comprehending the current nuclear landscape and the ongoing debates surrounding disarmament and non-proliferation.
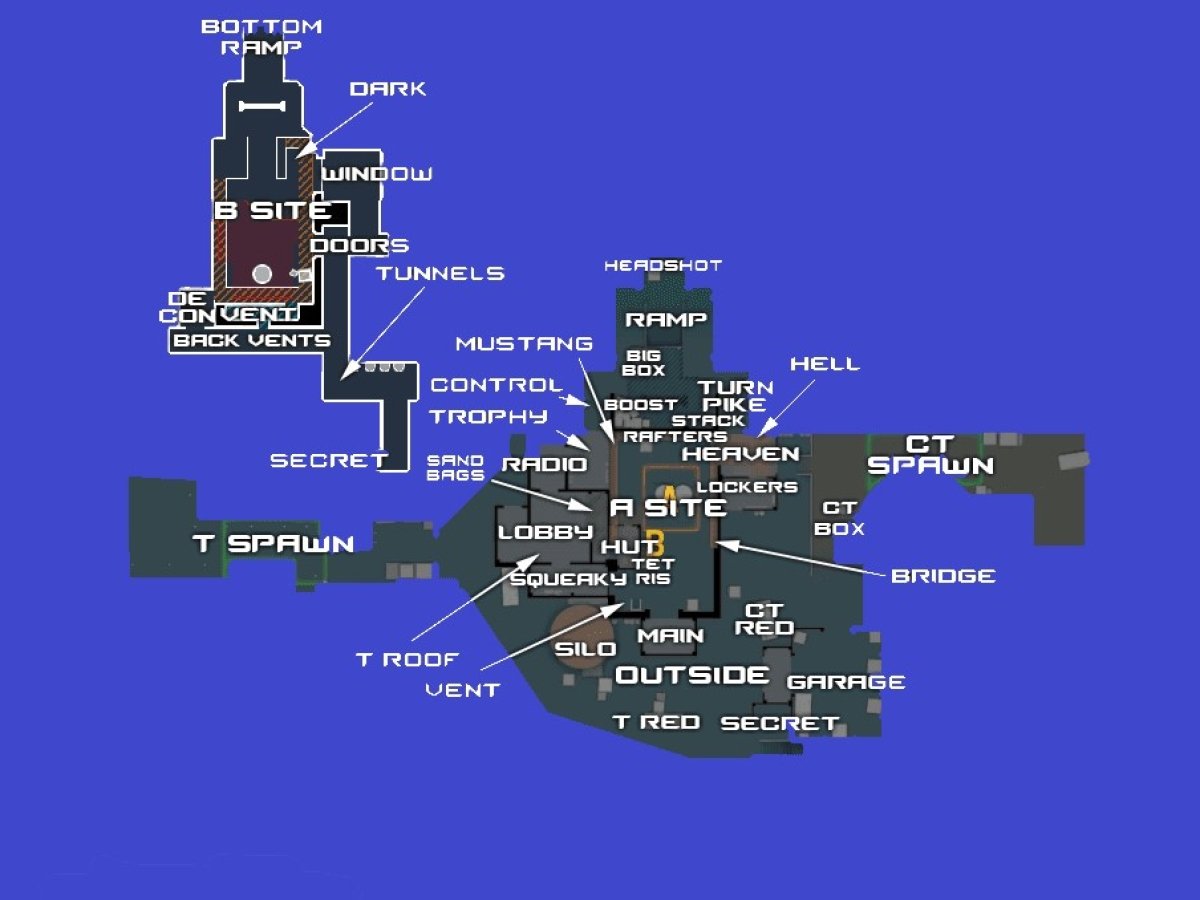
Counter-Strike is a popular multiplayer first-person shooter that pits teams of terrorists against counter-terrorists in various game modes. One interesting aspect of the game is the ability to engage in surf, a unique movement style that allows players to glide along ramps and perform tricks. The game has a rich history and a dedicated community that continuously evolves its competitive scene.
5 Little-Known Facts About Nuclear Proliferation You Need to Know
Nuclear proliferation refers to the spread of nuclear weapons and technology, and there are some little-known facts that may surprise you. First, did you know that the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) was opened for signature in 1968 and has been signed by 191 countries? This treaty aims to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons, promote peaceful uses of nuclear energy, and further the goal of disarmament. Despite its success, several countries have been able to develop nuclear arsenals outside of this framework, raising concerns about global security.
Another intriguing fact about nuclear proliferation is the role of non-state actors. While most discussions revolve around countries, terrorist organizations and rogue groups could potentially seek access to nuclear materials. In 2004, the A.Q. Khan network was uncovered, revealing how Pakistan's father of the atomic bomb had been secretly sharing nuclear technology with countries like Iran and Libya. This highlights the necessity for robust security measures and international collaboration to prevent these materials from falling into the wrong hands.
What Happens if a Nuclear Plant Meltdown Occurs?
A nuclear plant meltdown is a catastrophic failure that can occur in a nuclear reactor, leading to the release of radioactive materials into the environment. During a meltdown, the core of the reactor becomes overheated due to a loss of cooling, which can cause the fuel rods to become damaged and potentially melt. If this happens, the containment structures designed to prevent the escape of radiation can be compromised, resulting in severe consequences for the surrounding community and ecosystem. Understanding the aftermath of a nuclear plant meltdown is crucial for preparedness and disaster response.
In the event of a meltdown, immediate evacuation measures would be implemented in the affected area, often requiring emergency services to coordinate the safe relocation of thousands of residents. Additionally, long-term environmental impacts include soil and water contamination, which can lead to health hazards such as cancer and other illnesses for those exposed to radiation. Proper safety protocols, regular inspections, and advancements in nuclear technology are essential to mitigate the risks associated with nuclear plant meltdowns and ensure public safety.